Think back to the last time an interaction with a company, their products, and services really made you happy. What was so good about it and why? What were your expectations? Will you come back in the future? Chances are your great experience was the product of them endlessly asking these and many more questions, and then tweaking each step of the journey to satisfy you and other like-minded customers. In other words, their effort to become truly customer-centric.
Almost all businesses talk the talk of “customer comes first”, but many fail when it comes to walking the walk. It’s because becoming customer-centric requires changing the whole company culture, and that’s so much more than just copy-pasting messages on materials.
While there is no clear roadmap to a successful culture change, there certainly are proven approaches and ways to measure the journey. In this article, you’ll learn why and how you should put customers first, and see what top companies do to become truly customer-centric.
Understanding customer-centric culture
Customer-centric culture is a set of beliefs and actions prioritizing customers above all else. It’s about listening, understanding, and acting on customer needs, transforming them into great customer experiences and product features.
In a customer-centric culture, employees are encouraged to empathize with customers, anticipate their desires, and proactively seek ways to enhance their experience. The general focus is on building long-term customer relationships rather than focusing on short-term transactions.
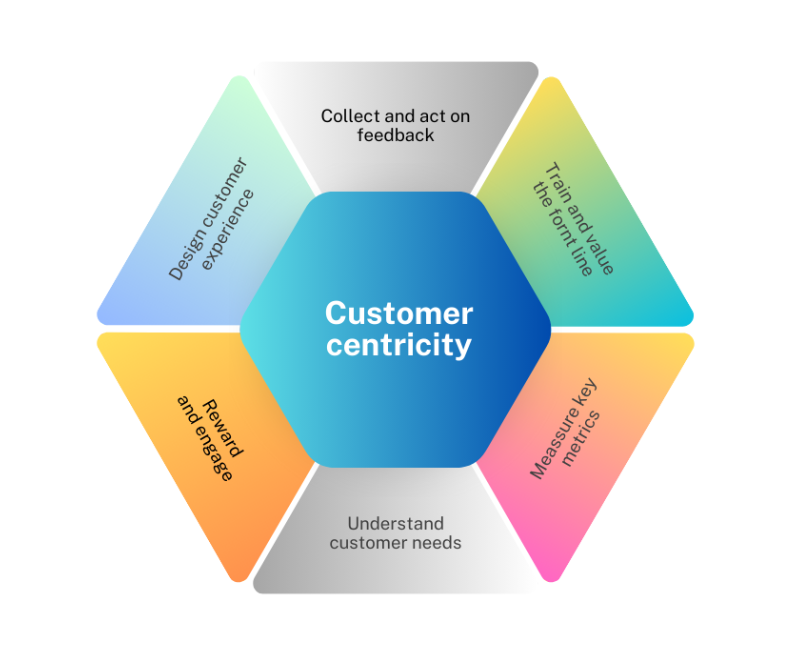
Why should you care about being a customer-centric company?
For businesses wanting to get ahead, creating a customer-centric culture is vital. In fact, 84% of businesses see rising revenue after investing in customer experience. While it may seem unintuitive at first, a loyal customer community brings in more revenue for your business in the long run. Loyal customers will become your advocates, practicing word-of-mouth marketing which ranks as the most trustworthy source.
A customer-centric culture doesn’t just benefit your ROI. It also benefits your employees. A study found that employees working in a customer-centric company feel more valued. Staff who feel valued are twice as likely to want to work for the same employer in two years.
Consumer power should not be underestimated, as customers won’t hesitate to stop supporting your business if they don’t feel valued. An organization that forgets about customers is destined to fail. They’ll build the wrong products, invest in the wrong resources, and lose customers while finding it hard to attract new ones.
Want to learn more? Then, check out our in-depth Customer service theory article.
How to create a customer-centric culture in your business
How can you be intentional about something so indefinite as culture? While there is no rulebook to follow, there are major areas to focus on and ways to measure your efforts. Here are the best approaches and real-life examples from top brands.
Meet and anticipate customer needs
Meeting customer needs means understanding their preferences, pain points, and expectations through active listening and engagement. Consult the members of your target audience, share this feedback with all teams and departments, and focus on adding improvements with customers in mind.
Great brands go even deeper and try to anticipate the needs, creating new standards in turn. Tim Cook, the CEO of Apple, said: “Our whole role in life is to give you something you didn’t know you wanted. And then once you get it, you can’t imagine your life without it”. Apple is the prime example of anticipating customer needs, but they’re also revered for their excellent customer service and not shying away from acting on feedback.
Be transparent and authentic
Some brands do everything in their power to hide from their customers, and if you happen to reach them, do the bare minimum possible. They put customer service behind ridiculous amounts of layers and communicate mostly through badly automated channels.
On the other spectrum, there are brands who communicate on a human level and take full accountability for their mistakes. A Twitter user shared their experience with Chewy, the online pet food retailer. After making a small mistake with his order, they sent the customer a handwritten sorry note, along with a discount code. Highlighting how much the little things truly matter, he claims this made him a customer for life. But this isn’t a one-off event. Going above and beyond is second nature for Chewy’s customer service representatives.

What are the main emotions and actions Chewy employees operate on? They don’t hide from customers and always approach them with authentic empathy. You can’t properly understand customer needs and concerns, much less make them feel heard and valued, if you don’t want to genuinely listen and help.
Invest in customer service training
It’s the frontline staff who meet customers, hear their concerns, and shape their experiences. Thanks to them, an identifiable pattern of customer-centricity can form. That’s why training customer service reps is a crucial step in introducing a customer-centric culture.
The training sessions might include workshops on empathy and active listening, mock scenarios, and role-playing exercises. When employees see the impact of positive experiences first-hand, they are more likely to go the extra mile in their own work.

The best example of empowered and eager customer service staff comes Zappos, the golden child of customer service done right since 2004. In fact, it might just be the most famous customer service story of all time. We’re talking about the longest customer call of all time, lasting over 10 hours, encompassing various topics, and creating a customer for life. The company not only allows, it encourages and fosters this kind of service because they know that a lifelong brand advocate is much more valuable than the 10 hours spent.
Businesses need to invest in employees and their well-being. In short, it’s hard to proactively create value if you don’t feel valued. Happy employees equating to happy customers goes tenfold in customer service.
When you create a sense of belonging within the organization, your employees will bring that feeling into the customer relationship as well. Moreover, businesses known for not valuing their frontline workers will sooner or later struggle to attract, let alone retain, employees.
Collect customer feedback
Customer feedback is possibly the most vital part of developing a customer-centric brand. You can’t understand your customers without listening to them, collecting feedback, and using it to gear your business strategy toward their needs.
Feedback gives you genuine, honest insights into your current performance rather than relying on assumptions. Don’t be afraid to let your customers know you’re not perfect and you are actively using their input to improve your business. In other words, make them feel heard.
There are countless platforms and ways in which customers choose to leave feedback. That’s why it’s important to share feedback across departments. For example, if customers repeatedly leave pricing feedback with the technical support representatives, it should make its way to the marketing department. Get customer service software to make documenting and sharing feedback easy.
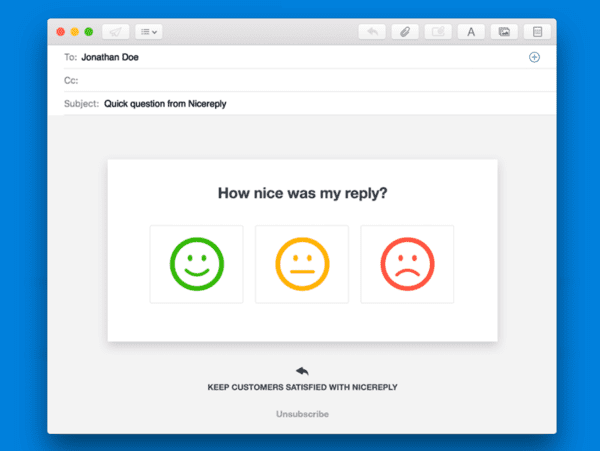
Common methods of collecting feedback are post-purchase surveys or emails, but follow-up calls or even meetings are also frequent. If unsure how to ask for feedback, try one of our free feedback email templates.
Align metrics with customer satisfaction
Despite the abstract nature of culture, there are ways to put a finger on its pulse. These metrics will allow you to see the bigger picture:
- Churn rate is the number of customers who leave your business during a certain period. A lower churn rate will reveal that your customer-centric efforts are successful in customer retention.
- Employee churn rate will uncover whether employees feel valued, happy, and motivated or have reasons to leave.
- Net promoter score (NPS) and Employee net promoter score (eNPS) are surveys allowing customers and employees to express how satisfied they are and how likely they are to recommend you.
- Customer lifetime value (CLV), measuring the total revenue an average customer creates will reveal how profitable customer retention is for your business.
Don’t forget to set goals and share the outcomes with your employees. Employees need to see their efforts linked to actual results and individual stories. Before anyone can be held accountable, you need to define what good results look like. To help you set customer service goals, see the top 16 customer service metrics.
Encourage customer referrals
Customer referrals are when satisfied customers recommend a product or service to others based on their positive interactions. They are not only a reward for a job well done but also a way to improve and keep the customer-centric culture running, as 73% of consumers are more likely to recommend brands with good loyalty programs.
In addition to creating a customer incentive to recommend your brand (such as a discount or a free sample), referral programs also help you quantify your customer-centric strategy.
Create a seamless customer experience
Customers have enough stress as is. What they need the least is businesses, which makes it even harder for them. We’ve talked about understanding your clients and collecting their feedback. Now it’s time to put this knowledge to good use.
A seamless customer experience is the compounded effort of all teams to understand and anticipate customer behavior and translate it into future experiences. From relevant marketing messaging and cleverly designed products to in-depth customer service.
Prioritize and execute the actions with the most impact on customer satisfaction and loyalty. Consider if your website is user-friendly and if customers report positive experiences with customer service. If you don’t have much feedback yet or need to make sense of the existing one, try creating buyer persona profiles or approaching existing customers directly.
Seamless experience can look like a lot of things. Let’s take Spotify as an example. They make discovering new music a seamless personalized experience. Your weekly discovery queue feels like a friend hand-picked it for you. These experiences make you feel seen, strengthen the emotional connection, and encourage you to continue using their app.
Opt for LiveAgent’s customer experience software
Seamless customer experience requires various moving parts to work in synergy. You need to be easily reachable on several channels, make both your live and automated communication empathetic and customer-centric. At the same time, make sure your customers do not need to repeat the information to several representatives, document any feedback, and make the feedback easily shareable among all teams. Only then can customer focus be translated into the products and services.
That’s a lot to keep in mind. That’s why it’s best to look for a software solution to handle all of these in one place. LiveAgent will help you centralize all of your customer interactions, share knowledge across departments, and make the insights easily accessible to everyone. This will make following up on your customer-centric strategies and promises much easier.
Nurture loyalty through rewards
Customer loyalty is the main goal of a customer-centric approach. Loyal customers make repeat purchases and recommend businesses, which makes it crucial to build a relationship beyond the initial purchase.
A rewards program is a great way to show your customers you value both their business and the relationship as a whole. Complementing reward programs with free samples, discount codes, and personalized experiences such as a birthday discount will make your customers feel even more valued.
A good example is LEGO, where customers are rewarded points not only for their purchases but also for registering their LEGO sets or getting involved in the community. Another interesting approach are the paid subscription loyalty programs, such as Amazon Prime which ensures fast and free delivery, loads of entertainment options, special discounts, and other benefits for a low monthly fee.
Use language that reassures your customers
The way brands interact with customers plays a big role in creating a customer-centric culture. If customers feel valued and understood, rather than just another cog in the wheel, they will be more engaged and inclined to keep supporting your business.
Use language that shows customers they mean a lot to you — acknowledge their issues, be empathetic, and thank them for their input. Always be positive, explain things in simple terms, and don’t be afraid to be human, mess up, and say sorry. Language goes a long way in showing customers that their well-being is your priority.
Stay adaptive and continuously improve
Without conscious upkeep, the customer-centric culture might just fade away. Continuously monitor your efforts to uncover any issues and space for improvements. Put yourself in the shoes of your customers and look for ways to lower their effort and make their experience even more pleasant. Don’t forget to value and celebrate frontline staff, and continuously create an environment allowing them to be genuine about providing great experiences.
Overcoming challenges and roadblocks
When driving a culture change, you are bound to be met with resistance. We’ve already covered the lack of communication between departments and insufficient accountability. Here are other common issues making organizations stuck and how to combat them:
- Leaders don’t understand front-line roles: Zeynep Ton, the author of The Case for Good Jobs, uncovered that leaders don’t trust frontline workers, seeing them as unfocused absentists. Meanwhile, it’s all just about the lack of understanding. To solve this issue, CEOs of companies such as Starbucks or Uber have pledged to spend more time with frontline employees.
- Not all departments participating: Typically only some departments focus on customers, but a true customer-centric culture needs to be the combined effort of all departments. Listening to feedback and baking user-friendly experiences into the product is more powerful than support staff patiently leading users through a hot mess of a product.
- Customer-centricity being just words: Some leaders are eager to jump on creating core values and refuse to do anything else while expecting their frontline staff to uphold the values. Customers will see right through this. Customer-centricity requires steady effort with tightly set processes, accountability, and constant revisions to stay the course.
Conclusion
The shift towards becoming a truly customer-centric organization is a complex, but truly rewarding process for all parties. When you focus on customers, everything else falls into place with happier employees and higher ROI. While it seems scary at first, even small changes can still have a great impact. The most challenging part is keeping tabs on all your customer experience efforts. To create memorable experiences and make collecting and sharing feedback easier, try LiveAgent with a 30-day free trial!
Shift to a customer-centric culture the easy way
Centralize your customer data, collect feedback, and provide great customer service all in one place! Our customer experience software will help you follow through on your customer-centric goals.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the difference between customer-centricity and customer focus?
Think of customer focus as the evolutionary step before customer-centricity. For customer-focused organizations, business goals are king, but these goals are derived from the needs and ideas of their customers. True customer-centricity bases the most value on customers, expecting other goals to fall in place as a by-product. You also might’ve heard of customer-obsession, which is just a fancy synonym for customer-centricity.
What are the stages of changing a company culture?
Culture change can generally be broken down into four stages. First, there is awareness of problems in your existing culture and defining the desired outcomes. Then there’s commitment, the stage where you plan and set processes. The third stage is all about the hard work of putting the commitments into practice. The last stage is evaluating progress. A culture is changed by repeatedly cycling through these stages and making sure you keep sustaining the culture.
What are the customer-centric culture values?
It’s a set of values highlighting the needs and feelings of your customers in everything you do. They include always being understanding, empathetic, and respectful in communication, listening to and acting on feedback, and going the extra mile to anticipate needs and create memorable experiences.
How do you promote a customer-centric culture?
Culture change is never easy and just pasting the words in the company's core values won’t be enough. Loads of training, feedback loops, and data analysis will need to take place until focusing on customers instead of product or sales becomes second nature. Growing pains can always be eased by celebrating success stories, and letting employees know their efforts are not in vain.
What can happen if the company doesn't establish a customer-centric culture?
There are hundreds, even thousands of companies doing the same thing you do. With fierce competition and the cost of acquiring new customers rising, creating a loyal customer community is a must if you want to survive. Customers know they have a choice and if you don’t make them feel valued, they won’t think twice to switch to someone who will.

 Български
Български  Čeština
Čeština  Dansk
Dansk  Deutsch
Deutsch  Eesti
Eesti  Español
Español  Français
Français  Ελληνικα
Ελληνικα  Hrvatski
Hrvatski  Italiano
Italiano  Latviešu
Latviešu  Lietuviškai
Lietuviškai  Magyar
Magyar  Nederlands
Nederlands  Norsk bokmål
Norsk bokmål  Polski
Polski  Română
Română  Русский
Русский  Slovenčina
Slovenčina  Slovenščina
Slovenščina  简体中文
简体中文  Tagalog
Tagalog  Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt  العربية
العربية  Português
Português 

